Over the last few years, technology has created new opportunities for healthcare improvements and the development of patient care systems. These include smart pills and ingestible sensors and they are considered to be revolutionary advancements in the field of health monitoring. Smart pills are designed to have sensors that help them take data readings within the body and relay this information to other servers in real time. While ingesting sensors are non-invasive and can help in diagnosing conditions from within the body. These devices are changing the way we look at health care and diagnosis, treatment, and management of diseases and conditions and hence are changing the face of health care.
Contents
Development and Technology Behind Smart Pills and Ingestible Sensors
The Evolution of Smart Pills and Ingestible Sensors
The idea behind the implementation of health monitoring devices that can be ingested goes back to the 90s, but actual development started only a few years ago. The initial concepts of the field concerned itself with the possibilities of non-invasive surveillance of internal health states. Smart pills’ use in practical applications started in the early 2000s with the primary focus on drug delivery and monitoring.
Some of the critical benchmarks include the discover of biocompatible materials, the downscaling of electronics, and the evolution of wireless applications. Some of the innovative firms in this field include Proteus Digital Health while research institutions such as MIT have also been involved. These are the pioneers who have set the platform for the current smart pills and ingestible sensors we have today and have contributed immensely to their creation and uses.
How Smart Pills Work
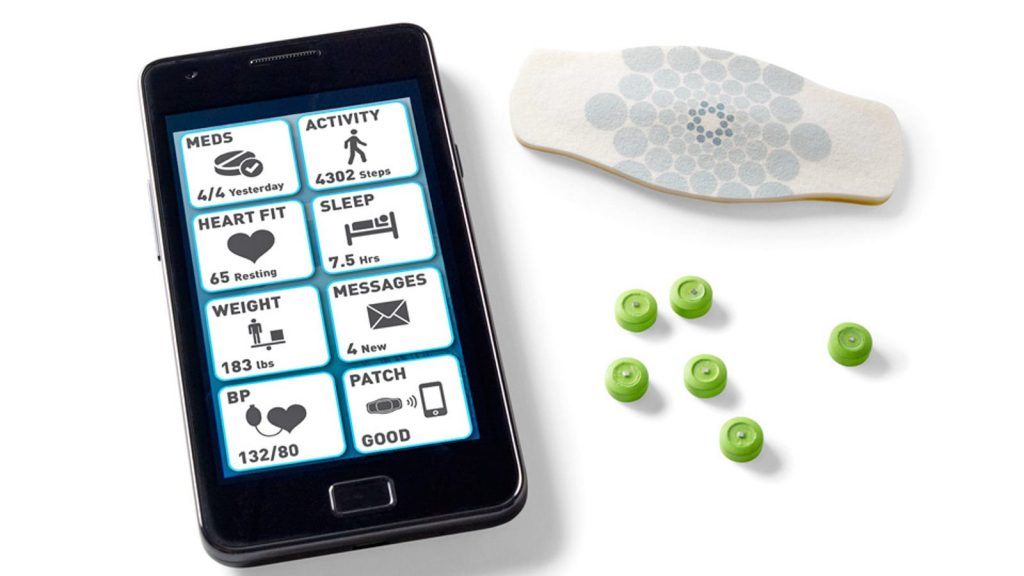
Smart pills are fitted with small sensors and electronic devices that can record numerous physiological factors including pH, temperature and the effectiveness of delivery of the medication. These are pills that can be swallowed and once they get into the body, they are able to send data to other external devices through wireless communication hence can be monitored in real time. There are smart pills that are used for monitoring the patients’ compliance with the medications and there are smart pills used for diagnosis like the PillCam that captures images of the gastrointestinal tract.
Subsequent developments in smart pill design are directed towards increasing the accuracy of the sensors, the longevity of the battery, and biocompatibility. Such developments make smart pills a rather useful application of IoT in the field of ambulatory care and precise treatment.
The Science Behind Ingestible Sensors
Ingestible sensors work on the principle of employing tiny electronic devices that are capable of detecting and transmitting the body’s internal parameters from the interior of the gastrointestinal system. These sensors are usually pH sensors, pressure sensors, and temperature sensors all of which are housed in a biocompatible housing. Ingestible sensors are better than other health monitoring technologies because they offer a better and more direct assessment of the internal body’s health.
For instance, they can provide constant surveillance of digestive health which is not possible with external devices. Some of the present uses are in diagnosing gastrointestinal diseases and in assessing the rectal temperature in intensive care unit patients. As it has been pointed out in the case studies, they are capable of delivering accurate and real-time information and thus their promise to transform the way health is monitored.
Monitoring and Transmitting Health Data
Real-Time Health Data Collection with Smart Pills
Smart pills have other features that include sensors that help in the detection of pH, temperature, and pressure among others. These devices are normally incorporated in the mobile and cloud platforms hence allowing for the transfer and storage of data. A smart pill is a capsule that has a sensor once the patient swallows it then the sensor starts recording data and the data is relayed to a smartphone or tablet via a wireless connection. This data can be further transmitted to the cloud servers for processing and storage in real-time and in the long run.
Some of the use cases have demonstrated that smart pills can help in the non-invasive tracking of patients’ compliance with the prescribed drugs and gastrointestinal disorders. For example, patients with chronic diseases have been able to be monitored continually for early interventions that have improved their health status. These devices provide an opportunity to save patients’ lives and health by providing non-invasive and efficient means for gathering important health information, changing the approach to patient’s health by doctors and nurses.
Wireless Communication and Data Security
In smart pills, wireless communication is the process of transferring data from the inside of the body to the outside world using RFID or Bluetooth. The security of data and patients’ confidentiality is of great importance as the transmission process relates to health information.
Measures of security such as data encryption and secure communication are used to ensure that this data is not accessed by unauthorized persons. However, issues like interference and stability of the signal within the body’s environment persist as some of the difficulties. Scientists are always developing these technologies to make them more reliable and secure so that patient’s health information is both correct and private.
Potential Benefits of Smart Pills and Ingestible Sensors in Healthcare
Advantages of Using Ingestible Sensors for Health Monitoring
Ingestible sensors bring a lot of changes to the increase in the accuracy of the collection of health data as compared to the traditional approaches. Since these devices give data that is in direct contact with the body, the information provided is real-time and accurate, thus enabling early diagnosis of diseases. For example, the smart pill can provide constant checking of GI tracts, and this helps in the early detection of diseases like Crohn’s disease and ulcers.
Furthermore, these devices are non-invasive hence patients will be more compliant and willing to use them without experiencing pain that comes with invasive procedures. It enables the healthcare providers to monitor the patients continuously and accurately and make the treatments more appropriate for the patient’s conditions and therefore enhances the quality of the patient care.
Transforming Chronic Disease Management
Of all the applications, smart pills and ingestible sensors are seen to have the greatest potential in the treatment of chronic ailments. For patients with such diseases as diabetes, hypertension and heart disease, these devices provide an opportunity to control several key health indicators and make timely adjustments to the treatment process. For instance, ingestible sensors can monitor the intake of medications, and therefore, patients will be in a position to take their medications correctly as prescribed especially when living with chronic diseases.
Furthermore, they can also track changes in the body and inform the healthcare providers of the possible complications before they progress to the next level. This proactive approach can save a lot of money in health care since people will not be taken through the ordeal of being admitted or treated under emergency circumstances. In conclusion, smart pills and ingestible sensors in chronic disease management not only improve the patient’s quality of life or prognosis but also aid in optimizing the health system for a lower cost.
Challenges and Considerations
Technical and Ethical Challenges
Smart pills and ingestible sensors are some of the innovations that have been displayed as promising; however, they bear some technical and ethical issues. Challenges which include the battery life of the sensors, and the reliability of the data collected and transmitted are technical and will need constant research and development. Some of the challenges that still require advancement include the shrinking of electronic parts and the establishment of reliable wireless communication within a body.
Ethical issues are also relevant because the ingestion of electronics raises concerns regarding the patient’s privacy and security of their data. Security of patients’ data is thus an essential factor that will help to win the public’s trust. Besides, there are issues like regulation that have to be resolved as well. These devices have to meet certain stringent tests and get approval from authorities such as the FDA. These regulatory pathways may be quite lengthy and expensive and this becomes a major challenge to the developers.
Patient Acceptance and Accessibility
Another determinant that requires consideration in the case of smart pills and ingestible sensors relates to patient acceptance. Patients’ worries and misconceptions regarding the swallowing of electronic devices must be addressed. Some patients may have negative attitudes towards these technologies due to misconceptions such as them being dangerous or invasive; therefore, the patients should be enlightened on the safety and benefits of these technologies.
Some of the ways in which the public can increase the accessibility and affordability of these devices is to lower the manufacturing costs and make these devices available through subsidies or insurance. With time, as its application increases, the prices are expected to decrease due to increased economies of scale.
Conclusion
Smart pills and ingestible sensors are revolutionizing the field of health and wellness due to their ability to offer real-time information from inside the human body. These are major advancements, which include; early diagnosis of diseases, better management of chronic diseases, and better patient compliance.
However, technical, ethical, and regulatory limitations cannot hold back progress and growing patient compliance that are leading to the integration of the technologies. In the course of research, there is hope for smart pills and ingestible sensors to transform the field of healthcare and enhance the quality of patient care.